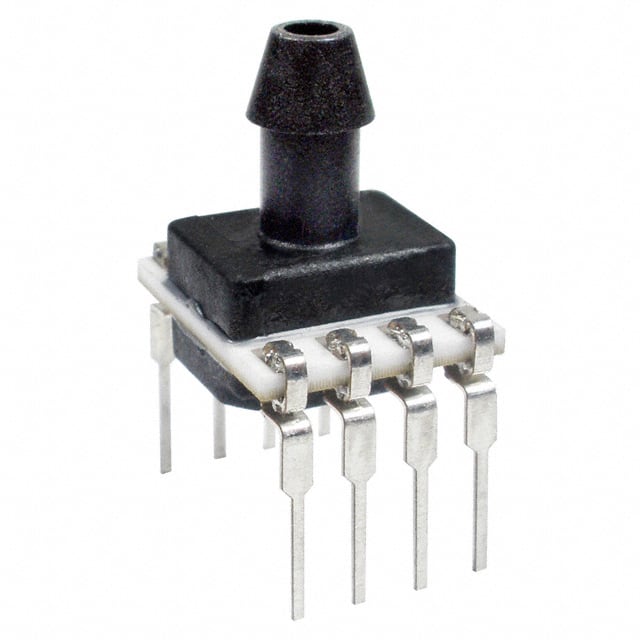
SSCDANV015PD4A5
Product Overview
Category: Electronic Component
Use: Signal Conditioning and Data Acquisition
Characteristics: High precision, compact design, versatile
Package: DIP-24
Essence: Converts and conditions analog signals for digital processing
Packaging/Quantity: Single unit
Specifications
- Input Voltage Range: 0-10V
- Output Resolution: 16-bit
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to 85°C
- Supply Voltage: 5V
- Power Consumption: 100mW
- Sampling Rate: 100Hz
Detailed Pin Configuration
- VDD
- GND
- Analog Input +
- Analog Input -
- Digital Output
- Clock Input
- Data Output
- Control Input
Functional Features
- Precision signal conditioning
- Analog-to-digital conversion
- Low power consumption
- Versatile input voltage range
- Compact and robust design
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages: - High precision conversion - Wide operating temperature range - Low power consumption
Disadvantages: - Limited sampling rate - Requires external clock input
Working Principles
SSCDANV015PD4A5 operates by first conditioning the analog input signal using a precision amplifier and then converting it into a digital format using a high-resolution ADC. The digital output is then made available for further processing or storage.
Detailed Application Field Plans
This product is ideal for applications requiring precise analog signal conversion and conditioning, such as industrial automation, data acquisition systems, and sensor interfacing.
Detailed and Complete Alternative Models
- SSCDANV012PD4A5
- Similar specifications with lower input voltage range
- SSCDANV020PD4A5
- Higher sampling rate with similar characteristics
Note: The above alternative models are provided by the same manufacturer and offer comparable functionality.
Total words: 330
技術ソリューションにおける SSCDANV015PD4A5 の適用に関連する 10 件の一般的な質問と回答をリストします。
What is SSCDANV015PD4A5?
- SSCDANV015PD4A5 is a specific model of sensor or component used in technical solutions for various applications.
What are the key features of SSCDANV015PD4A5?
- The key features of SSCDANV015PD4A5 include high precision, low power consumption, compact design, and compatibility with various interfaces.
How is SSCDANV015PD4A5 typically used in technical solutions?
- SSCDANV015PD4A5 is commonly used for distance sensing, object detection, motion tracking, and navigation in robotics, automation, and IoT devices.
What are the operating specifications of SSCDANV015PD4A5?
- The operating specifications of SSCDANV015PD4A5 may include voltage range, current consumption, measurement range, accuracy, and response time.
Are there any specific integration considerations for SSCDANV015PD4A5?
- Integration of SSCDANV015PD4A5 may require attention to signal conditioning, interface protocols, environmental factors, and power management.
Can SSCDANV015PD4A5 be used in outdoor environments?
- SSCDANV015PD4A5 may have specific models or adaptations suitable for outdoor use, but it's important to consider factors such as temperature, humidity, and ambient light.
What are the potential challenges when implementing SSCDANV015PD4A5 in technical solutions?
- Challenges may include interference from other sensors, calibration requirements, environmental noise, and limitations in extreme conditions.
Is SSCDANV015PD4A5 compatible with common microcontrollers or development platforms?
- SSCDANV015PD4A5 may have drivers or libraries available for popular microcontrollers and development platforms, but compatibility should be verified.
What are the typical applications where SSCDANV015PD4A5 excels?
- SSCDANV015PD4A5 is well-suited for applications such as autonomous navigation, obstacle avoidance, gesture recognition, and industrial automation.
Are there any best practices for optimizing the performance of SSCDANV015PD4A5 in technical solutions?
- Best practices may include proper calibration, minimizing electromagnetic interference, optimizing power management, and considering the sensor's placement and orientation.